Research
Research topics:
Biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease and related disorders
Development of experimental therapies for PD and ALS: from cell cultures to clinical studies
Mechanisms of axonal degeneration: role of autophagy and axonal transport
Transition metals as pathogenic factors in Parkinson’s disease
Axonal regeneration in CNS projections
Some of Our Current Research Questions:
What is the role of calcium, CRMP2 and specific autophagy proteins in axonal degeneration? Read More >
Can we improve imaging readouts in living animals to better understand axonal pathology? Read More >
Are Rho kinase inhibitors putative treatment targets in PD, ALS and CNS trauma? Read More >
How does alpha-synuclein regulate axonal stability, regeneration, autophagy, vesicle release? Read More >
How does alpha-synuclein interact with transition metals in vitro and in vivo? Read More >
Can we improve the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease using innovative biomarkers? Read More >
Tools & Models:
In vitro: primary cell cultures (RGC, MDN, HC, cortex), scratch model for regeneration, nucleofection of primary neurons, molecular biology, protein analysis
In vivo: ON axotomy, ON crush, peripheral nerve graft, spinal cord hemisection, ALS mouse model (SOD1 G93A), PD models (6-OHDA, MPTP, A53T, A30P), AAV-mediated gene transfer and gene knockdown, gene regulation by siRNA and miRNA, stereotactical brain injections
Imaging: life-imaging of the optic nerve, synchrotron-based XRF and SAXS of primary cultures and tissue
Collection of biological samples (CSF, blood, tear fluid) for biomarker analyses in Parkinson’s disease and related disorders
Development of experimental therapies for PD and ALS: translation from preclinical studies to clinical trials
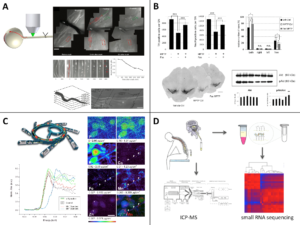
Figure:
A: Life-imaging of the optic nerve permits to visualize single axons and follows their degeneration over several hours (Koch 2011 Nature Protocols).
B: The MPTP model is a prime example for a toxin-based animal model, which we use to assess the effects of novel therapeutic substances, e.g. the rho kinase inhibitor Fasudil (Tönges 2012 Brain).
C: Synchrotron radiation is a powerful tool for the generation of high-resolution x-ray fluorescence images, e.g. to study the subcellular distribution of trace metals (Ducic 2015 ACS Chem Neurosci).
D: Cerebrospinal fluid is used as a source for biomarkers, which is analysed, e.g for elemental content by ICP-MS and for small RNA by next-generation sequencing.
Collaborators
Prof. Dr. Stefan Bonn
Dr. Asunción Carmona
Prof. Dr. Donato Di Monte
Dr. Rosanna Dono
Prof. Dr. André Fischer
Dr. Sebastian Kügler
Dr. Andreas Leha
Dr. Christof Lenz
Prof. Dr. Katrin Marcus
Prof. Dr. Bernhard Michalke
Prof. Dr. Uwe Michel
Prof. Dr. Hans Werner Müller
Dr. Richard Ortega
Prof. Dr. Tiago Outeiro
Prof. Dr. Silvio Rizzoli
Prof. Dr. Tim Salditt
Prof. Dr. Henning Urlaub
Prof. Dr. Markus Weber
Prof. Dr. Inga Zerr
Prof. Dr. Markus Zweckstetter